What Is An XML File And How Do I Open One
In this article, we will discuss XML files, their advantages, common uses and how to open an XML file format. Click to read full guide.
Author:Daniel BarrettApr 30, 20222819 Shares201339 Views

Nowadays, many professions require at least some proficiency with computers and technology. Therefore, the XML file format is used in the workplace for various reasons.
Understanding what XML is and how to use XML files can help you navigate a technologically-advanced workplace.
This article will discuss XML files, their advantages, common XML uses, and how to open an XML file.
What’s An XML File?
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and was created by the W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) in the 90s.
Though XML, like HTML, is a human-readable markup language, they serve very different purposes. HTML describes the structure of a web page and its content, and XML describes data structure.
XML provides programs, and more importantly, programmers, a standard, widely accepted format to transmit data across different systems. In that way, XML has more in common with JSON than HTML.
Don’t miss: How To Export Bookmarks From Chrome
While XML is no longer the preferred method for organizing and transmitting data, it still has its place. XML is still used in many legacy systems, and both RSS and SVG are based on the XML format.
What Are The Differences Between HTML And XML
- Purpose: With HTML, or hypertext markup language, information is displayed, but with XML, that information is transferred.
Typically, HTML is used for encoding web pages. On the other hand, XML is a language for data description used to store data.
- Ability to customize: HTML uses a pre-selected range of markup symbols or shortcodes, which describe the presentation of a web page’s content.
Conversely, XML is extensible and allows users to customize and create markup symbols.
With XML, users have complete control and can create an unlimited symbol set to describe their content.
Also read: How To Easily Convert A WMA File To MP3
Advantages Of XML
Using XML files is advantageous for many reasons, including:
- Readability: The data must be easily accessible and readable for a data analyst. XML files are easy to comprehend because they use human language with actual words instead of a computer language.
For example, XML tag names clearly define and explain the data. Moreover, each tag is arranged to come before its data, so the information is neat and organized.
Additionally, computers efficiently process XML files because the data is exchanged straightforwardly with the XML markup language.
- Compatibility: XML files are compatible with Java and are completely portable, meaning you can access and transport data at any time and from any location.
All you need is applications that can process XML, and then you can store and transmit your data.
- Customization: As an extensible markup language, XML allows users to create their tags or use tags created by other users.
If you are using tags from other users, you will need to make sure that the tags are using the natural language of your domain and that they have the features you require.
Users can create an unlimited amount of tags in XML.
Don’t miss: How To Reset A Forgotten Windows 10 Password
Common Uses Of XML
XML has multiple uses across a wide range of web pages and applications. Some common uses of XML include:
- Web publishing: With XML, users can create and customize interactive web pages. Once the data is stored by XML, you can manipulate the content for different users or multiple devices.
You will need to make sure that you check the style sheet processing along the way.
It may be helpful to use an extensible style sheet language transformation processor, which will allow you to transform the XML file into other layouts, such as HTML for web pages.
In a business, using XML format in this way would be the web developer’s job.
- Web tasks: XML may be used for web searching and automating tasks. In this way, XML examines the information in a file, making it easier to get top results when performing a web search.
For instance, if a user conducts a web search for an author named Jim Green using HTML, the search results page may show other occurrences of “green” aside from the author.
But if you use XML, web searches are limited to the information you want, which is the information found in the tag.
- General applications: All kinds of applications can benefit from XML as it offers a streamlined method of accessing information.
This straightforward process allows both applications and devices to utilize, store, transfer, and display data. For example, data architects and programmers use XML daily in the workplace.
How To Open An XML File
Working with XML files is relatively simple, even for a beginner. A couple of different methods for opening an XML file format are opening the file and editing with a text editor or opening and viewing the file with a web browser.
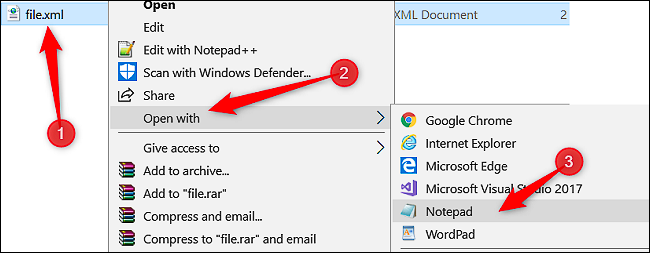
The steps for opening an XML file with a text editor include:
- Right-click the XML file you want to open.
- Point to “Open With” on the context menu.
- Click the “Notepad” option.
The Notepad and Notepad++ text editors are good options to open XML files. However, in Notepad, you can open the XML file, but the formatting may become chaotic and confusing.
In this case, it may be better to use Notepad++ because it stays true to the file’s original formatting. Here is what the XML file opened in Notepad++ looks like:
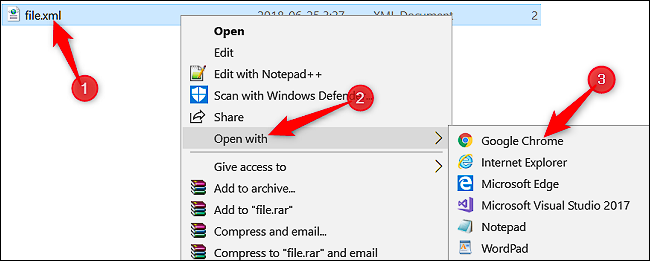
The steps for opening an XML file to view in a web browser include:
- Open your default web browser.
- Double-click on the XML file, and it should open in your browser.
- If it does not open, right-click on the file to find a list of options for opening it with other programs.
- Now you will be able to select your web browser from the list of programs. It is essential to understand how to use XML files in the workplace in today’s technologically advanced society.
There are many benefits of using XML, and thankfully, working with XML files is a straightforward process.
Users have a couple of different options for opening and viewing XML files, depending on their technology preferences.
Kindly share your experiences in the comment section if you found this article helpful.
Editor’s picks:

Daniel Barrett
Author
Latest Articles
Popular Articles