Technology Is Evolving Fast - The Kurzweil Theory About Technology Evolution
Smartphones as we know them today did not exist ten years ago.In the past three decades, nobody even owned a computer. Consider that the introduction of the first personal computers was roughly 40 years ago, technology is evolving fast. Everyone appears to be staring at a luminous mobile computer these days.
Author:Daniel BarrettNov 22, 20224.9K Shares291.6K Views
Smartphonesas we know them today did not exist ten years ago.In the past three decades, nobody even owned a computer. Consider that the introduction of the first personal computers was roughly 40 years ago, technology is evolving fast. Everyone appears to be staring at a luminous mobile computer these days.
Technology Is Evolving Fast - The Kurzweil Theory
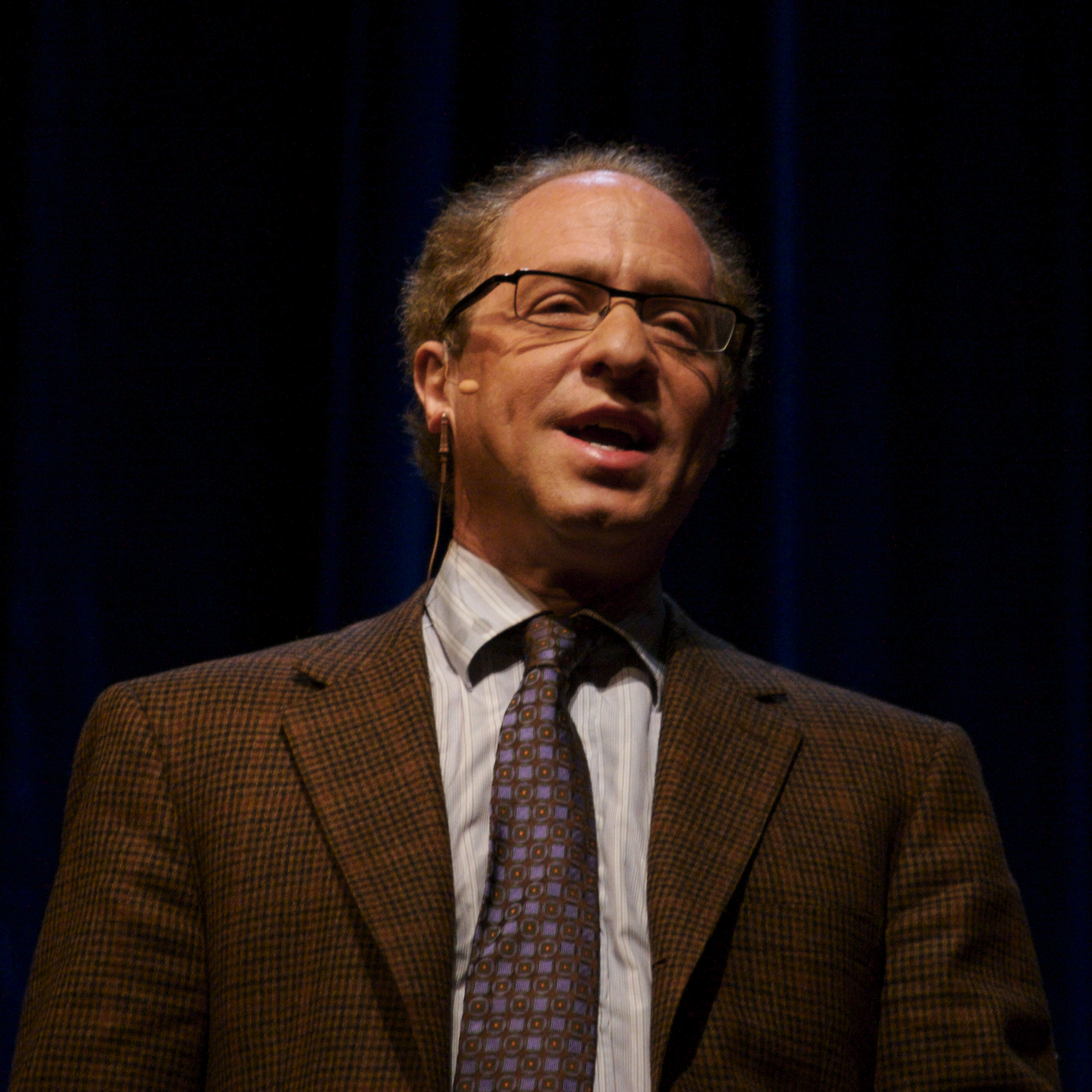
It seems as though technology is developing more quickly than ever. Is this true, though? Ray Kurzweilclaims that it most definitely is. Kurzweil demonstrates the accelerating pace of technology in his book The Singularity Is Near and explains the driving reason behind it.
This article will examine the unforeseen effects of the rapid pace of technology as well as Kurzweil's explanation of this driving factor, which he called the law of accelerating returns.
Moore's Law Is Well Known, Yet It Is Not Unique
The cost of computer chips has decreased as their power has increased. This is due to the fact that over the past 50 years, the quantity of transistors tiny electrical components that carry out fundamental operations on a single chip has been steadily increasing.
Moore's Law, which predicts exponential growth, explains why a modern smartphone can afford to fit so many mind-boggling capabilities into such a small space.
The development of technology in computer chips is well recognized, but strangely, they are not an exception.
Various other technologies, whether they store bits of data or record DNA basepairs, exhibit similar exponential expansion. The result is the same: in only a few decades, capabilities have expanded by the thousands, millions, and billions for less money.
What's Happening, Then?
According to the rule of accelerating returns, because a single force is propelling technical development forward, it advances exponentially over time, especially in the area of information technology. It turns out that being exponential is all about evolution.
Natural "technologies" are refined by biology. Genes, which are the blueprints for useful tools, are stored in the DNA of living things. Advantageous innovations are transmitted to offspring as a result of selective pressure, sometimes known as "survival of the fittest."
Incredible growth occurs when this process unfolds across geological spans, generation after generation, in a chaotic yet gradual manner.
Rather than starting over, organisms have evolved to become more sophisticated and capable throughout time by building on genetic development. Today, we can see this inventive power almost wherever we turn.
Technology was developed from biology's countless breakthroughs, including cells, bones, eyes, thumbs, and brains.
Like biology, technology is likewise subject to evolution, but according to Kurzweil, it does so far more quickly. Stationzilla a reputed science research mediait's implicated in the study of biology in techdeveloping.
By "repurposing" the innovations and ideas of their forebears, civilizations advance. Similar to this, every technological generation builds on the innovations of earlier generations, which results in an improvement cycle.
The central tenet of Kurzweil's theory is that each new generation of technology builds upon its forerunners, allowing for the development of ever-superior technology in the following generations.
Technological development is accelerating exponentially.The rate of development between each generation of technology accelerates because each generation outperforms the previous one.
To understand this, consider building a chair using hand tools, power tools, and finally assembly lines. After each stage, the production rate increases.
Imagine that each iteration of these tools is also utilized to develop newer, higher-quality tools. According to Kurzweil, this mechanism is at work when engineers utilize software and computers to create ever-faster computer processors.
The technology's "returns" (such as speed, efficiency, price-performance, and overall "power"), which also advance exponentially, can be used to assess this acceleration.
Additionally, a technology gains popularity as it becomes more useful. As a result, an abundance of fresh resources is being invested in advancing the technology, including higher R&D budgets, the hiring of top people, etc.
This influx of additional resources initiates a "second stage" of exponential development, where the exponent, which measures the rate of exponential growth, starts to increase.
Specific paradigms, like integrated circuits, won't continue to expand exponentially, though. They develop until their potential is reached, at which time a new paradigm replaces the previous one.
The Law Of Increasing Returns Has Unexpected Consequences
"We won't experience 100 years of advancement in the 21st century it will be more like 20,000 years of progress (at today's rate)," stated Kurzweil in 2001, noting that our overall rate of growth doubled every ten years.
This implies that the future of incredibly potent technologies may be closer than we think. Although many of Ray Kurzweil's forecasts from the previous 25 years were accurate, some may have seemed far-fetched at the time.
For example, in 1990, he predicted that a computer would defeat a professional chess player by 1998, a prediction that was realized when IBM's Deep Blue defeated Garry Kasparov.
Even though the 21st century is only 15 years old, the advancements have been very astounding, including the widespread use of cellphones, the Internet, increasingly nimble robots, and AI that can learn.
At a cost of hundreds of millions of dollars, we sequenced the first human genome in 2004. Currently, machines can sequence 18,000 genomes annually for $1,000.
People Also Ask
Is Technology Evolving Too Fast?
More than 60% of those surveyed expressed concern that governments don't comprehend technology well enough to regulate it and that technological advancement is moving too quickly.
Another 66% of respondents expressed concern that technology will make it impossible to verify the veracity of what people are hearing or seeing.
Is Technology Constantly Evolving?
Regardless of the state of the economy or the market, technology is constantly changing. Innovative new technologies are being developed to address global concerns.
How Technology Is Evolving The World?
Smartwatches and smartphones are examples of multipurpose devices made possible by modern technology.
Computers are now more powerful, portable, and faster than ever before. Technology has aided in all of these revolutions by making our lives simpler, faster, better, and more enjoyable.
Conclusion
These are only a few instances of how the law of accelerating returns propels development. Because the future is approaching much faster than we anticipate, it is critical to consider where we are going and how we will get there exponentially.

Daniel Barrett
Author
Daniel Barrett is a tech writer focusing on IoT, gadgets, software, and cryptocurrencies. With a keen interest in emerging technologies, Daniel offers expert analysis and commentary on industry trends. Follow him for authoritative insights into the latest tech innovations.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles

