IPv4 vs IPv6: Everything You Need to Know
This article compares two kinds of IP addresses IPv4 vs IPv6, and also talks about their definitions, their benefits and their differences
Author:Daniel BarrettJul 15, 202270.7K Shares1.4M Views
IPv4 vs IPv6: You must probably have heard of IP address maybe in a sci-fi movie at least. An IP (Internet Protocol) address is the numerical tag that is assigned to every device. The device must be one that can use the IP to communicate. The IP address represents your device for a specific network. It is sometimes referred to IP number or Internet address. This article compares two kinds of IP addresses IPv4 vs IPv6, and also talks about their definitions, their benefits and their differences.
IP address specifies the technical format of the addressing and packets scheme. Most networks combine IP with a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). It also allows developing a virtual connection between a destination and a source.
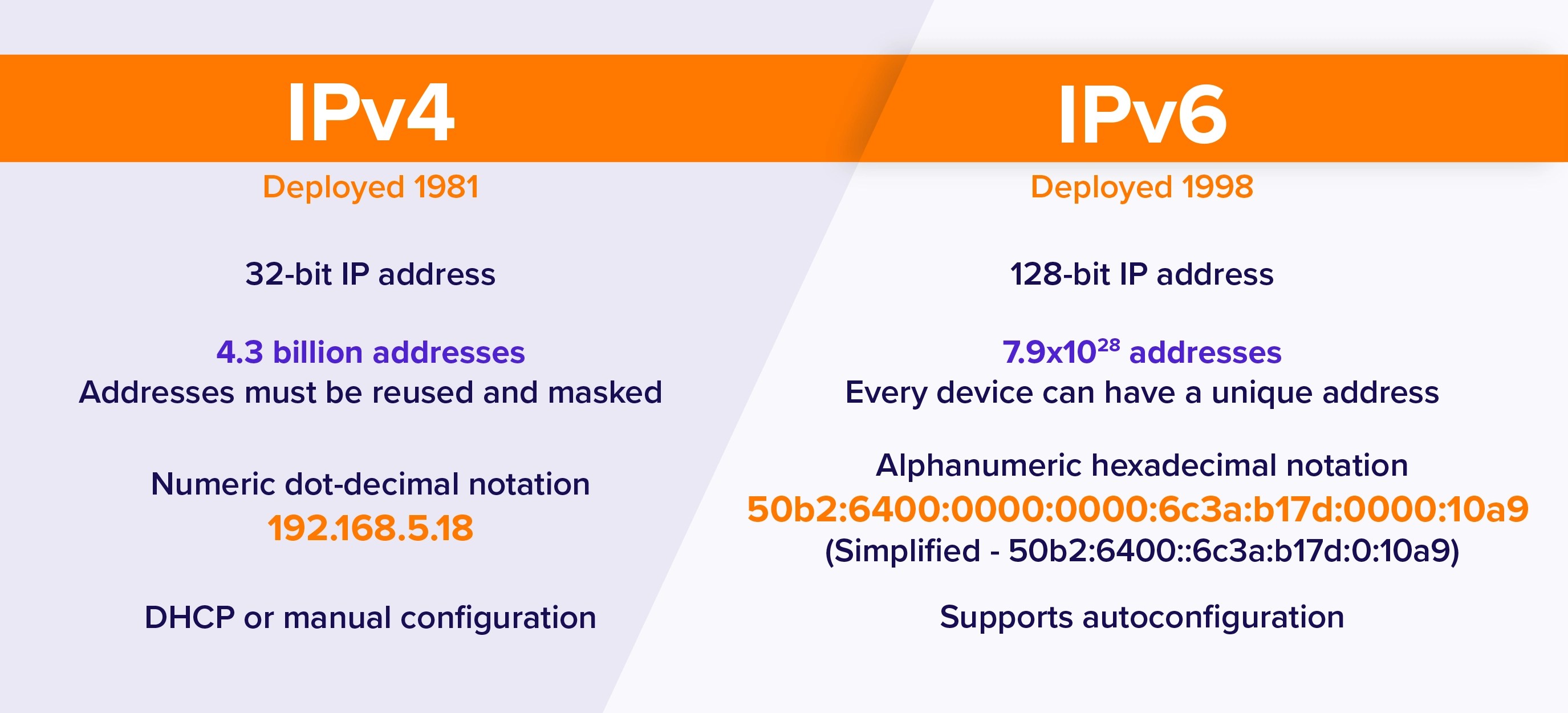
IPv4 vs IPv6: Key Difference
The IPv4
IPv4 is short for Internet Protocol version 4. It is the intangible technology that makes it possible for us to connect our devices to the web. Whenever you log on to the Internet with your device, it is assigned a unique, numerical IP address such as 99.48.227.227. To send data from one computer to another through the web, a data packet must be transferred across the network containing the IP addresses of both devices.
Features of the IPv4
Below are the features of IPv4:
- No true connection protocols.
- Ability to establish a simple communication layer over different devices.
- It doesn’t require much memory.
- It possesses quick access to addresses.
- Packaged video libraries and conferences.
- It is supported by millions of devices if not all.
The IPv6
IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol. This new IP address version is being released to accomplish the need for more Internet addresses. It was developed to resolve issues that are associated with IPv4. With 128-bit address space, it allows 340 undecillion unique address space. IPv6 is also called IPng (Internet Protocol next generation).
Internet Engineer Taskforce initiated it in early 1994. The design and development of that suite are now called IPv6.
Features of IPv6
Below are the features of IPv6:
- Ordered addressing and routing model
- Stateful and Stateless configuration
- Compatible with quality of service (QoS)
- An ideal protocol for neighboring node interaction
Major Benefits of IPv6
- Disbanded NAT (Network Address Translation)
- Auto-configuration
- Disbanded private address collisions
- An improved multicast routing
- Easier header format
- Simplified, more efficient routing
- True quality of service (QoS), also called “flow labeling”
- Built-in authentication and privacy support
- Easily changeable options and extensions
- Easier administration (no more DHCP)
IPv4 Vs IPv6: Major Disparities
Having stated their abilities, here are the significant differences between IPv4 and IPv6:
- The IPv4 is a 32-Bit IP address while IPv6 is a 128-Bit IP address.
- IPv4 implements a numeric addressing method while IPv6 uses an alphanumeric addressing method.
- IPv4 binary bits are separated by a dot(.) while IPv6 binary bits are separated by a colon(:).
- The IPv4 offers 12 header fields while IPv6 offers 8 header fields.
- There is a support for broadcast in the IPv4 while IPv6 doesn’t support broadcast.
- There is the presence of checksum fields in IPv4 while IPv6 doesn’t have checksum fields
- When we compare IPv4 and IPv6, IPv4 supports VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) whereas IPv6 doesn’t support VLSM.
- IPv4 uses ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) to map to MAC address whereas IPv6 uses NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) to map to MAC address.
Bottom Line
The IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the sixth revision to the Internet Protocol and is to take over from the IPv4. It functions similarly to IPv4 in that it provides the unique IP addresses necessary for Internet-enabled devices to communicate. However, there is one distinguishing factor: it utilizes a 128-bit IP address.
IPv4 uses a 32-bit address for its Internet addresses. In true sense, it can provide support for 2^32 IP addresses in total around 4.29 billion. At first glance, this should be enough, but all 4.29 billion IP addresses have now been assigned, leading to the address shortage issues we face today.
On the other hand, IPv6 utilizes 128-bit Internet addresses. Therefore, it can support 2^128 Internet addresses—340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 of them to be exact. The number of IPv6 addresses is 1028 times larger than the number of IPv4 addresses. So, this figure should sustain us for a longer period of time.
The text form of the IPv6 address is xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx, where each x represents a hexadecimal digit, representing 4 bits. Leading zeros can be omitted. The double colon (::) can be used once in the text form of an address, to designate any number of 0 bits.
Editor’s picks:

Daniel Barrett
Author
Daniel Barrett is a tech writer focusing on IoT, gadgets, software, and cryptocurrencies. With a keen interest in emerging technologies, Daniel offers expert analysis and commentary on industry trends. Follow him for authoritative insights into the latest tech innovations.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles